Mercury is the smallest planet in the Solar System and the closest to the Sun. Its orbit around the Sun takes 87.97 Earth days, the shortest of all the Sun’s planets. It is named after the Roman god Mercurius (Mercury), god of commerce, messenger of the gods, and mediator between gods and mortals, corresponding to the Greek god Hermes (Ἑρμῆς). Like Venus, Mercury orbits the Sun within Earth’s orbit as an inferior planet, and its apparent distance from the Sun as viewed from Earth never exceeds 28°. This proximity to the Sun means the planet can only be seen near the western horizon after sunset or the eastern horizon before sunrise, usually in twilight. At this time, it may appear as a bright star-like object, but is more difficult to observe than Venus. From Earth, the planet telescopically displays the complete range of phases, similar to Venus and the Moon, which recurs over its synodic period of approximately 116 days.
Mercury rotates in a way that is unique in the Solar System. It is tidally locked with the Sun in a 3:2 spin–orbit resonance, meaning that relative to the fixed stars, it rotates on its axis exactly three times for every two revolutions it makes around the Sun. As seen from the Sun, in a frame of reference that rotates with the orbital motion, it appears to rotate only once every two Mercurian years. An observer on Mercury would therefore see only one day every two Mercurian years.
Mercury’s axis has the smallest tilt of any of the Solar System’s planets (about 1⁄30 degree). Its orbital eccentricity is the largest of all known planets in the Solar System;[b] at perihelion, Mercury’s distance from the Sun is only about two-thirds (or 66%) of its distance at aphelion. Mercury’s surface appears heavily cratered and is similar in appearance to the Moon‘s, indicating that it has been geologically inactive for billions of years. Having almost no atmosphere to retain heat, it has surface temperatures that vary diurnally more than on any other planet in the Solar System, ranging from 100 K (−173 °C; −280 °F) at night to 700 K (427 °C; 800 °F) during the day across the equatorial regions. The polar regions are constantly below 180 K (−93 °C; −136 °F). The planet has no known natural satellites.
Two spacecraft have visited Mercury: Mariner 10 flew by in 1974 and 1975; and MESSENGER, launched in 2004, orbited Mercury over 4,000 times in four years before exhausting its fuel and crashing into the planet’s surface on April 30, 2015. The BepiColombo spacecraft is planned to arrive at Mercury in 2025.

Mercury in true color (by MESSENGER in 2008)
 The ancients knew Mercury by different names depending on whether it was an evening star or a morning star. By about 350 BC, the ancient Greeks had realized the two stars were one.[23] They knew the planet as Στίλβων Stilbōn, meaning “twinkling”, and Ἑρμής Hermēs, for its fleeting motion, a name that is retained in modern Greek (Ερμής Ermis). The Romans named the planet after the swift-footed Roman messenger god, Mercury (Latin Mercurius), which they equated with the Greek Hermes, because it moves across the sky faster than any other planet. The astronomical symbol for Mercury is a stylized version of Hermes’ caduceus; a Christian cross was added in the 16th century:
The ancients knew Mercury by different names depending on whether it was an evening star or a morning star. By about 350 BC, the ancient Greeks had realized the two stars were one.[23] They knew the planet as Στίλβων Stilbōn, meaning “twinkling”, and Ἑρμής Hermēs, for its fleeting motion, a name that is retained in modern Greek (Ερμής Ermis). The Romans named the planet after the swift-footed Roman messenger god, Mercury (Latin Mercurius), which they equated with the Greek Hermes, because it moves across the sky faster than any other planet. The astronomical symbol for Mercury is a stylized version of Hermes’ caduceus; a Christian cross was added in the 16th century: ![]()
Mercury is one of four terrestrial planets in the Solar System, and is a rocky body like Earth. It is the smallest planet in the Solar System, with an equatorial radius of 2,439.7 kilometres (1,516.0 mi). Mercury is also smaller—albeit more massive—than the largest natural satellites in the Solar System, Ganymede and Titan. Mercury consists of approximately 70% metallic and 30% silicate material.
Mercury appears to have a solid silicate crust and mantle overlying a solid, iron sulfide outer core layer, a deeper liquid core layer, and a solid inner core. The planet’s density is the second highest in the Solar System at 5.427 g/cm3, only slightly less than Earth’s density of 5.515 g/cm3. If the effect of gravitational compression were to be factored out from both planets, the materials of which Mercury is made would be denser than those of Earth, with an uncompressed density of 5.3 g/cm3 versus Earth’s 4.4 g/cm3. Mercury’s density can be used to infer details of its inner structure. Although Earth’s high density results appreciably from gravitational compression, particularly at the core, Mercury is much smaller and its inner regions are not as compressed. Therefore, for it to have such a high density, its core must be large and rich in iron.
Geologists estimate that Mercury’s core occupies about 55% of its volume; for Earth this proportion is 17%. Research published in 2007 suggests that Mercury has a molten core. Surrounding the core is a 500–700 km (310–430 mi) mantle consisting of silicates. Based on data from the Mariner 10 mission and Earth-based observation, Mercury’s crust is estimated to be 35 km (22 mi) thick. However, this model may be an overestimate and the crust could be 26 ± 11 km (16.2 ± 6.8 mi) thick based on an Airy isostacy model. One distinctive feature of Mercury’s surface is the presence of numerous narrow ridges, extending up to several hundred kilometers in length. It is thought that these were formed as Mercury’s core and mantle cooled and contracted at a time when the crust had already solidified.
 Mercury’s core has a higher iron content than that of any other major planet in the Solar System, and several theories have been proposed to explain this. The most widely accepted theory is that Mercury originally had a metal–silicate ratio similar to common chondrite meteorites, thought to be typical of the Solar System’s rocky matter, and a mass approximately 2.25 times its current mass.[43] Early in the Solar System’s history, Mercury may have been struck by a planetesimal of approximately 1/6 that mass and several thousand kilometers across. The impact would have stripped away much of the original crust and mantle, leaving the core behind as a relatively major component. A similar process, known as the giant impact hypothesis, has been proposed to explain the formation of the Moon.
Mercury’s core has a higher iron content than that of any other major planet in the Solar System, and several theories have been proposed to explain this. The most widely accepted theory is that Mercury originally had a metal–silicate ratio similar to common chondrite meteorites, thought to be typical of the Solar System’s rocky matter, and a mass approximately 2.25 times its current mass.[43] Early in the Solar System’s history, Mercury may have been struck by a planetesimal of approximately 1/6 that mass and several thousand kilometers across. The impact would have stripped away much of the original crust and mantle, leaving the core behind as a relatively major component. A similar process, known as the giant impact hypothesis, has been proposed to explain the formation of the Moon.
Alternatively, Mercury may have formed from the solar nebula before the Sun’s energy output had stabilized. It would initially have had twice its present mass, but as the protosun contracted, temperatures near Mercury could have been between 2,500 and 3,500 K and possibly even as high as 10,000 K. Much of Mercury’s surface rock could have been vaporized at such temperatures, forming an atmosphere of “rock vapor” that could have been carried away by the solar wind.
A third hypothesis proposes that the solar nebula caused drag on the particles from which Mercury was accreting, which meant that lighter particles were lost from the accreting material and not gathered by Mercury. Each hypothesis predicts a different surface composition, and there are two space missions set to make observations. MESSENGER, which ended in 2015, found higher-than-expected potassium and sulfur levels on the surface, suggesting that the giant impact hypothesis and vaporization of the crust and mantle did not occur because potassium and sulfur would have been driven off by the extreme heat of these events. BepiColombo, which will arrive at Mercury in 2025, will make observations to test these hypotheses. The findings so far would seem to favor the third hypothesis; however, further analysis of the data is needed.
Mercury’s surface is similar in appearance to that of the Moon, showing extensive mare-like plains and heavy cratering, indicating that it has been geologically inactive for billions of years. It is more heterogeneous than either Mars‘s or the Moon’s, both of which contain significant stretches of similar geology, such as maria and plateaus.[49] Albedo features are areas of markedly different reflectivity, which include impact craters, the resulting ejecta, and ray systems. Larger albedo features correspond to higher reflectivity plains.Mercury has dorsa (also called “wrinkle-ridges“), Moon-like highlands, montes (mountains), planitiae (plains), rupes (escarpments), and valles (valleys).
MASCS spectrum scan of Mercury’s surface by MESSENGER
The planet’s mantle is chemically heterogeneous, suggesting the planet went through a magma ocean phase early in its history. Crystallization of minerals and convective overturn resulted in layered, chemically heterogeneous crust with large-scale variations in chemical composition observed on the surface. The crust is low in iron but high in sulfur, resulting from the stronger early chemically reducing conditions than is found in the other terrestrial planets. The surface is dominated by iron-poor pyroxene and olivine, as represented by enstatite and forsterite, respectively, along with sodium-rich plagioclase and minerals of mixed magnesium, calcium, and iron-sulfide. The less reflective regions of the crust are high in carbon, most likely in the form of graphite.
Names for features on Mercury come from a variety of sources. Names coming from people are limited to the deceased. Craters are named for artists, musicians, painters, and authors who have made outstanding or fundamental contributions to their field. Ridges, or dorsa, are named for scientists who have contributed to the study of Mercury. Depressions or fossae are named for works of architecture. Montes are named for the word “hot” in a variety of languages. Plains or planitiae are named for Mercury in various languages. Escarpments or rupēs are named for ships of scientific expeditions. Valleys or valles are named for abandoned cities, towns, or settlements of antiquity.
Mercury was heavily bombarded by comets and asteroids during and shortly following its formation 4.6 billion years ago, as well as during a possibly separate subsequent episode called the Late Heavy Bombardment that ended 3.8 billion years ago. Mercury received impacts over its entire surface during this period of intense crater formation,facilitated by the lack of any atmosphere to slow impactors down. During this time Mercury was volcanically active; basins were filled by magma, producing smooth plains similar to the maria found on the Moon. An unusual crater with radiating troughs has been discovered that scientists called “the spider”. It was later named Apollodorus.
Craters on Mercury range in diameter from small bowl-shaped cavities to multi-ringed impact basins hundreds of kilometers across. They appear in all states of degradation, from relatively fresh rayed craters to highly degraded crater remnants. Mercurian craters differ subtly from lunar craters in that the area blanketed by their ejecta is much smaller, a consequence of Mercury’s stronger surface gravity. According to International Astronomical Union (IAU) rules, each new crater must be named after an artist who was famous for more than fifty years, and dead for more than three years, before the date the crater is named.
The largest known crater is Caloris Planitia, or Caloris Basin, with a diameter of 1,550 km. The impact that created the Caloris Basin was so powerful that it caused lava eruptions and left a concentric mountainous ring ~2 km tall surrounding the impact crater. The floor of the Caloris Basin is filled by a geologically distinct flat plain, broken up by ridges and fractures in a roughly polygonal pattern. It is not clear whether they are volcanic lava flows induced by the impact or a large sheet of impact melt.
At the antipode of the Caloris Basin is a large region of unusual, hilly terrain known as the “Weird Terrain”. One hypothesis for its origin is that shock waves generated during the Caloris impact traveled around Mercury, converging at the basin’s antipode (180 degrees away). The resulting high stresses fractured the surface. Alternatively, it has been suggested that this terrain formed as a result of the convergence of ejecta at this basin’s antipode.
Overall, 46 impact basins have been identified. A notable basin is the 400 km wide, multi-ring Tolstoj Basin that has an ejecta blanket extending up to 500 km from its rim and a floor that has been filled by smooth plains materials. Beethoven Basin has a similar-sized ejecta blanket and a 625 km diameter rim. Like the Moon, the surface of Mercury has likely incurred the effects of space weathering processes, including solar wind and micrometeorite impacts.
There are two geologically distinct plains regions on Mercury.[ Gently rolling, hilly plains in the regions between craters are Mercury’s oldest visible surfaces, predating the heavily cratered terrain. These inter-crater plains appear to have obliterated many earlier craters, and show a general paucity of smaller craters below about 30 km in diameter.
Smooth plains are widespread flat areas that fill depressions of various sizes and bear a strong resemblance to the lunar maria. Unlike lunar maria, the smooth plains of Mercury have the same albedo as the older inter-crater plains. Despite a lack of unequivocally volcanic characteristics, the localisation and rounded, lobate shape of these plains strongly support volcanic origins. All the smooth plains of Mercury formed significantly later than the Caloris basin, as evidenced by appreciably smaller crater densities than on the Caloris ejecta blanket.

Tolstoj basin is along the bottom of this image of Mercury’s limb
One unusual feature of Mercury’s surface is the numerous compression folds, or rupes, that crisscross the plains. As Mercury’s interior cooled, it contracted and its surface began to deform, creating wrinkle ridges and lobate scarps associated with thrust faults. The scarps can reach lengths of 1000 km and heights of 3 km. These compressional features can be seen on top of other features, such as craters and smooth plains, indicating they are more recent. Mapping of the features has suggested a total shrinkage of Mercury’s radius in the range of ~1 to 7 km. Most activity along the major thrust systems probably ended about 3.6–3.7 billion years ago.Small-scale thrust fault scarps have been found, tens of meters in height and with lengths in the range of a few km, that appear to be less than 50 million years old, indicating that compression of the interior and consequent surface geological activity continue to the present.
The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter discovered that similar but smaller thrust faults exist on the Moon.
There is evidence for pyroclastic flows on Mercury from low-profile shield volcanoes. 51 pyroclastic deposits have been identified,where 90% of them are found within impact craters.A study of the degradation state of the impact craters that host pyroclastic deposits suggests that pyroclastic activity occurred on Mercury over a prolonged interval.
A “rimless depression” inside the southwest rim of the Caloris Basin consists of at least nine overlapping volcanic vents, each individually up to 8 km in diameter. It is thus a “compound volcano“. The vent floors are at least 1 km below their brinks and they bear a closer resemblance to volcanic craters sculpted by explosive eruptions or modified by collapse into void spaces created by magma withdrawal back down into a conduit. Scientists could not quantify the age of the volcanic complex system but reported that it could be of the order of a billion years.

The surface temperature of Mercury ranges from 100 to 700 K (−173 to 427 °C; −280 to 800 °F)[19] at the most extreme places: 0°N, 0°W, or 180°W. It never rises above 180 K at the poles, due to the absence of an atmosphere and a steep temperature gradient between the equator and the poles. The subsolar point reaches about 700 K during perihelion (0°W or 180°W), but only 550 K at aphelion (90° or 270°W). On the dark side of the planet, temperatures average 110 K. The intensity of sunlight on Mercury’s surface ranges between 4.59 and 10.61 times the solar constant (1,370 W·m−2).
Although the daylight temperature at the surface of Mercury is generally extremely high, observations strongly suggest that ice (frozen water) exists on Mercury. The floors of deep craters at the poles are never exposed to direct sunlight, and temperatures there remain below 102 K, far lower than the global average. This creates a cold trap where ice can accumulate. Water ice strongly reflects radar, and observations by the 70-meter Goldstone Solar System Radar and the VLA in the early 1990s revealed that there are patches of high radar reflection near the poles. Although ice was not the only possible cause of these reflective regions, astronomers think it was the most likely.
The icy regions are estimated to contain about 1014–1015 kg of ice, and may be covered by a layer of regolith that inhibits sublimation. By comparison, the Antarctic ice sheet on Earth has a mass of about 4×1018 kg, and Mars’s south polar cap contains about 1016 kg of water.[86] The origin of the ice on Mercury is not yet known, but the two most likely sources are from outgassing of water from the planet’s interior or deposition by impacts of comets.
Mercury is too small and hot for its gravity to retain any significant atmosphere over long periods of time; it does have a tenuous surface-bounded exosphere containing hydrogen, helium, oxygen, sodium, calcium, potassium and others[15][16] at a surface pressure of less than approximately 0.5 nPa (0.005 picobars). This exosphere is not stable—atoms are continuously lost and replenished from a variety of sources. Hydrogen atoms and helium atoms probably come from the solar wind, diffusing into Mercury’s magnetosphere before later escaping back into space. Radioactive decay of elements within Mercury’s crust is another source of helium, as well as sodium and potassium. MESSENGER found high proportions of calcium, helium, hydroxide, magnesium, oxygen, potassium, silicon and sodium. Water vapor is present, released by a combination of processes such as: comets striking its surface, sputtering creating water out of hydrogen from the solar wind and oxygen from rock, and sublimation from reservoirs of water ice in the permanently shadowed polar craters. The detection of high amounts of water-related ions like O+, OH−, and H3O+ was a surprise. Because of the quantities of these ions that were detected in Mercury’s space environment, scientists surmise that these molecules were blasted from the surface or exosphere by the solar wind.
Sodium, potassium and calcium were discovered in the atmosphere during the 1980–1990s, and are thought to result primarily from the vaporization of surface rock struck by micrometeorite impacts including presently from Comet Encke. In 2008, magnesium was discovered by MESSENGER. Studies indicate that, at times, sodium emissions are localized at points that correspond to the planet’s magnetic poles. This would indicate an interaction between the magnetosphere and the planet’s surface.
On November 29, 2012, NASA confirmed that images from MESSENGER had detected that craters at the north pole contained water ice. MESSENGER‘s principal investigator Sean Solomon is quoted in The New York Times estimating the volume of the ice to be large enough to “encase Washington, D.C., in a frozen block two and a half miles deep”.
Despite its small size and slow 59-day-long rotation, Mercury has a significant, and apparently global, magnetic field. According to measurements taken by Mariner 10, it is about 1.1% the strength of Earth’s. The magnetic-field strength at Mercury’s equator is about 300 nT Like that of Earth, Mercury’s magnetic field is dipolar. Unlike Earth’s, Mercury’s poles are nearly aligned with the planet’s spin axis. Measurements from both the Mariner 10 and MESSENGER space probes have indicated that the strength and shape of the magnetic field are stable.
It is likely that this magnetic field is generated by a dynamo effect, in a manner similar to the magnetic field of Earth. This dynamo effect would result from the circulation of the planet’s iron-rich liquid core. Particularly strong tidal heating effects caused by the planet’s high orbital eccentricity would serve to keep part of the core in the liquid state necessary for this dynamo effect.
Mercury’s magnetic field is strong enough to deflect the solar wind around the planet, creating a magnetosphere. The planet’s magnetosphere, though small enough to fit within Earth, is strong enough to trap solar wind plasma. This contributes to the space weathering of the planet’s surface.[99] Observations taken by the Mariner 10 spacecraft detected this low energy plasma in the magnetosphere of the planet’s nightside. Bursts of energetic particles in the planet’s magnetotail indicate a dynamic quality to the planet’s magnetosphere.[96]
During its second flyby of the planet on October 6, 2008, MESSENGER discovered that Mercury’s magnetic field can be extremely “leaky”. The spacecraft encountered magnetic “tornadoes” – twisted bundles of magnetic fields connecting the planetary magnetic field to interplanetary space – that were up to 800 km wide or a third of the radius of the planet. These twisted magnetic flux tubes, technically known as flux transfer events, form open windows in the planet’s magnetic shield through which the solar wind may enter and directly impact Mercury’s surface via magnetic reconnectionThis also occurs in Earth’s magnetic field. The MESSENGER observations showed the reconnection rate is ten times higher at Mercury, but its proximity to the Sun only accounts for about a third of the reconnection rate observed by MESSENGER.

Graph showing relative strength of Mercury’s magnetic field
Mercury has the most eccentric orbit of all the planets in the Solar System; its eccentricity is 0.21 with its distance from the Sun ranging from 46,000,000 to 70,000,000 km (29,000,000 to 43,000,000 mi). It takes 87.969 Earth days to complete an orbit. The diagram illustrates the effects of the eccentricity, showing Mercury’s orbit overlaid with a circular orbit having the same semi-major axis. Mercury’s higher velocity when it is near perihelion is clear from the greater distance it covers in each 5-day interval. In the diagram, the varying distance of Mercury to the Sun is represented by the size of the planet, which is inversely proportional to Mercury’s distance from the Sun. This varying distance to the Sun leads to Mercury’s surface being flexed by tidal bulges raised by the Sun that are about 17 times stronger than the Moon’s on Earth.[104] Combined with a 3:2 spin–orbit resonance of the planet’s rotation around its axis, it also results in complex variations of the surface temperature. The resonance makes a single solar day (the length between two meridian transits of the Sun) on Mercury last exactly two Mercury years, or about 176 Earth days.
Mercury’s orbit is inclined by 7 degrees to the plane of Earth’s orbit (the ecliptic), the largest of all eight known solar planets.As a result, transits of Mercury across the face of the Sun can only occur when the planet is crossing the plane of the ecliptic at the time it lies between Earth and the Sun, which is in May or November. This occurs about every seven years on average.
Mercury’s axial tilt is almost zero,with the best measured value as low as 0.027 degrees.This is significantly smaller than that of Jupiter, which has the second smallest axial tilt of all planets at 3.1 degrees. This means that to an observer at Mercury’s poles, the center of the Sun never rises more than 2.1 arcminutes above the horizon.


At certain points on Mercury’s surface, an observer would be able to see the Sun peek up a little more than two-thirds of the way over the horizon, then reverse and set before rising again, all within the same Mercurian day. This is because approximately four Earth days before perihelion, Mercury’s angular orbital velocity equals its angular rotational velocity so that the Sun’s apparent motion ceases; closer to perihelion, Mercury’s angular orbital velocity then exceeds the angular rotational velocity. Thus, to a hypothetical observer on Mercury, the Sun appears to move in a retrograde direction. Four Earth days after perihelion, the Sun’s normal apparent motion resumes. A similar effect would have occurred if Mercury had been in synchronous rotation: the alternating gain and loss of rotation over revolution would have caused a libration of 23.65° in longitude.
For the same reason, there are two points on Mercury’s equator, 180 degrees apart in longitude, at either of which, around perihelion in alternate Mercurian years (once a Mercurian day), the Sun passes overhead, then reverses its apparent motion and passes overhead again, then reverses a second time and passes overhead a third time, taking a total of about 16 Earth-days for this entire process. In the other alternate Mercurian years, the same thing happens at the other of these two points. The amplitude of the retrograde motion is small, so the overall effect is that, for two or three weeks, the Sun is almost stationary overhead, and is at its most brilliant because Mercury is at perihelion, its closest to the Sun. This prolonged exposure to the Sun at its brightest makes these two points the hottest places on Mercury. Maximum temperature occurs when the Sun is at an angle of about 25 degrees past noon due to diurnal temperature lag, at 0.4 Mercury days and 0.8 Mercury years past sunrise. Conversely, there are two other points on the equator, 90 degrees of longitude apart from the first ones, where the Sun passes overhead only when the planet is at aphelion in alternate years, when the apparent motion of the Sun in Mercury’s sky is relatively rapid. These points, which are the ones on the equator where the apparent retrograde motion of the Sun happens when it is crossing the horizon as described in the preceding paragraph, receive much less solar heat than the first ones described above.
Mercury attains inferior conjunction (nearest approach to Earth) every 116 Earth days on average, but this interval can range from 105 days to 129 days due to the planet’s eccentric orbit. Mercury can come as near as 82,200,000 kilometres (0.549 astronomical units; 51.1 million miles) to Earth, and that is slowly declining: The next approach to within 82,100,000 km (51.0 million miles) is in 2679, and to within 82,000,000 km (51 million miles) in 4487, but it will not be closer to Earth than 80,000,000 km (50 million miles) until 28,622. Its period of retrograde motion as seen from Earth can vary from 8 to 15 days on either side of inferior conjunction. This large range arises from the planet’s high orbital eccentricity. Essentially because Mercury is closest to the Sun, when taking an average over time, Mercury is the closest planet to the Earth,[114] and—in that measure—it is the closest planet to each of the other planets in the Solar System.
The longitude convention for Mercury puts the zero of longitude at one of the two hottest points on the surface, as described above. However, when this area was first visited, by Mariner 10, this zero meridian was in darkness, so it was impossible to select a feature on the surface to define the exact position of the meridian. Therefore, a small crater further west was chosen, called Hun Kal, which provides the exact reference point for measuring longitude. The center of Hun Kal defines the 20° west meridian. A 1970 International Astronomical Union resolution suggests that longitudes be measured positively in the westerly direction on Mercury.The two hottest places on the equator are therefore at longitudes 0° W and 180° W, and the coolest points on the equator are at longitudes 90° W and 270° W. However, the MESSENGER project uses an east-positive convention.
For many years it was thought that Mercury was synchronously tidally locked with the Sun, rotating once for each orbit and always keeping the same face directed towards the Sun, in the same way that the same side of the Moon always faces Earth. Radar observations in 1965 proved that the planet has a 3:2 spin-orbit resonance, rotating three times for every two revolutions around the Sun. The eccentricity of Mercury’s orbit makes this resonance stable—at perihelion, when the solar tide is strongest, the Sun is nearly still in Mercury’s sky.
The rare 3:2 resonant tidal locking is stabilized by the variance of the tidal force along Mercury’s eccentric orbit, acting on a permanent dipole component of Mercury’s mass distribution.[123] In a circular orbit there is no such variance, so the only resonance stabilized in such an orbit is at 1:1 (e.g., Earth–Moon), when the tidal force, stretching a body along the “center-body” line, exerts a torque that aligns the body’s axis of least inertia (the “longest” axis, and the axis of the aforementioned dipole) to point always at the center. However, with noticeable eccentricity, like that of Mercury’s orbit, the tidal force has a maximum at perihelion and therefore stabilizes resonances, like 3:2, ensuring that the planet points its axis of least inertia roughly at the Sun when passing through perihelion.
The original reason astronomers thought it was synchronously locked was that, whenever Mercury was best placed for observation, it was always nearly at the same point in its 3:2 resonance, hence showing the same face. This is because, coincidentally, Mercury’s rotation period is almost exactly half of its synodic period with respect to Earth. Due to Mercury’s 3:2 spin-orbit resonance, a solar day lasts about 176 Earth days. A sidereal day (the period of rotation) lasts about 58.7 Earth days.
Simulations indicate that the orbital eccentricity of Mercury varies chaotically from nearly zero (circular) to more than 0.45 over millions of years due to perturbations from the other planets. This was thought to explain Mercury’s 3:2 spin-orbit resonance (rather than the more usual 1:1), because this state is more likely to arise during a period of high eccentricity. However, accurate modeling based on a realistic model of tidal response has demonstrated that Mercury was captured into the 3:2 spin-orbit state at a very early stage of its history, within 20 (more likely, 10) million years after its formation.
Numerical simulations show that a future secular orbital resonant perihelion interaction with Jupiter may cause the eccentricity of Mercury’s orbit to increase to the point where there is a 1% chance that the planet will collide with Venus within the next five billion years.
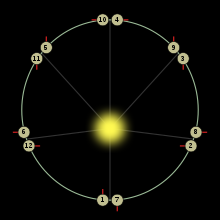
After one orbit, Mercury has rotated 1.5 times, so after two complete orbits the same hemisphere is again illuminated.
In 1859, the French mathematician and astronomer Urbain Le Verrier reported that the slow precession of Mercury’s orbit around the Sun could not be completely explained by Newtonian mechanics and perturbations by the known planets. He suggested, among possible explanations, that another planet (or perhaps instead a series of smaller ‘corpuscules’) might exist in an orbit even closer to the Sun than that of Mercury, to account for this perturbation. (Other explanations considered included a slight oblateness of the Sun.) The success of the search for Neptune based on its perturbations of the orbit of Uranus led astronomers to place faith in this possible explanation, and the hypothetical planet was named Vulcan, but no such planet was ever found.
The perihelion precession of Mercury is 5,600 arcseconds (1.5556°) per century relative to Earth, or 574.10±0.65 arcseconds per century relative to the inertial ICRF. Newtonian mechanics, taking into account all the effects from the other planets, predicts a precession of 5,557 arcseconds (1.5436°) per century. In the early 20th century, Albert Einstein‘s general theory of relativity provided the explanation for the observed precession, by formalizing gravitation as being mediated by the curvature of spacetime. The effect is small: just 42.98 arcseconds per century for Mercury; it therefore requires a little over twelve million orbits for a full excess turn. Similar, but much smaller, effects exist for other Solar System bodies: 8.62 arcseconds per century for Venus, 3.84 for Earth, 1.35 for Mars, and 10.05 for 1566 Icarus.
 Mercury’s apparent magnitude is calculated to vary between −2.48 (brighter than Sirius) around superior conjunction and +7.25 (below the limit of naked-eye visibility) around inferior conjunction. The mean apparent magnitude is 0.23 while the standard deviation of 1.78 is the largest of any planet. The mean apparent magnitude at superior conjunction is −1.89 while that at inferior conjunction is +5.93.[14] Observation of Mercury is complicated by its proximity to the Sun, as it is lost in the Sun’s glare for much of the time. Mercury can be observed for only a brief period during either morning or evening twilight.
Mercury’s apparent magnitude is calculated to vary between −2.48 (brighter than Sirius) around superior conjunction and +7.25 (below the limit of naked-eye visibility) around inferior conjunction. The mean apparent magnitude is 0.23 while the standard deviation of 1.78 is the largest of any planet. The mean apparent magnitude at superior conjunction is −1.89 while that at inferior conjunction is +5.93.[14] Observation of Mercury is complicated by its proximity to the Sun, as it is lost in the Sun’s glare for much of the time. Mercury can be observed for only a brief period during either morning or evening twilight.
Mercury can, like several other planets and the brightest stars, be seen during a total solar eclipse.[137]
Like the Moon and Venus, Mercury exhibits phases as seen from Earth. It is “new” at inferior conjunction and “full” at superior conjunction. The planet is rendered invisible from Earth on both of these occasions because of its being obscured by the Sun, except its new phase during a transit.
Mercury is technically brightest as seen from Earth when it is at a full phase. Although Mercury is farthest from Earth when it is full, the greater illuminated area that is visible and the opposition brightness surge more than compensates for the distance. The opposite is true for Venus, which appears brightest when it is a crescent, because it is much closer to Earth than when gibbous.
Nonetheless, the brightest (full phase) appearance of Mercury is an essentially impossible time for practical observation, because of the extreme proximity of the Sun. Mercury is best observed at the first and last quarter, although they are phases of lesser brightness. The first and last quarter phases occur at greatest elongation east and west of the Sun, respectively. At both of these times Mercury’s separation from the Sun ranges anywhere from 17.9° at perihelion to 27.8° at aphelion.At greatest western elongation, Mercury rises at its earliest before sunrise, and at greatest eastern elongation, it sets at its latest after sunset.
Mercury is more often and easily visible from the Southern Hemisphere than from the Northern. This is because Mercury’s maximum western elongation occurs only during early autumn in the Southern Hemisphere, whereas its greatest eastern elongation happens only during late winter in the Southern Hemisphere. In both of these cases, the angle at which the planet’s orbit intersects the horizon is maximized, allowing it to rise several hours before sunrise in the former instance and not set until several hours after sundown in the latter from southern mid-latitudes, such as Argentina and South Africa.
An alternate method for viewing Mercury involves observing the planet during daylight hours when conditions are clear, ideally when it is at its greatest elongation. This allows the planet to be found easily, even when using telescopes with 8 cm (3.1 in) apertures. However, great care must be taken to obstruct the Sun from sight because of the extreme risk for eye damage. This method bypasses the limitation of twilight observing when the ecliptic is located at a low elevation (e.g. on autumn evenings).
Ground-based telescope observations of Mercury reveal only an illuminated partial disk with limited detail. The first of two spacecraft to visit the planet was Mariner 10, which mapped about 45% of its surface from 1974 to 1975. The second is the MESSENGER spacecraft, which after three Mercury flybys between 2008 and 2009, attained orbit around Mercury on March 17, 2011, to study and map the rest of the planet.
The Hubble Space Telescope cannot observe Mercury at all, due to safety procedures that prevent its pointing too close to the Sun.[
Because the shift of 0.15 revolutions in a year makes up a seven-year cycle (0.15 × 7 ≈ 1.0), in the seventh year Mercury follows almost exactly (earlier by 7 days) the sequence of phenomena it showed seven years before.

© 2021 Tüm hakları saklıdır.